About TAR format
TAR is
a popular archiving
format, mainstream for data backup and distribution purpose on Unix and
Unix-like systems, as BSD, Linux and derivates. In use since early Unix
versions, predating integrated archiving and compression formats like
zip and rar, it
was
later standardized by POSIX-1.1988 and POSIX.1-2001. Tar packages are
sometimes referred as "tarballs".
"Tarbomb" refers to a tar
package
purposely built to spam extraction directory with a large number of
files, effect that can be avoided by moders archivers simply employing
"extract to new folder" option.
Maximum size of a
TAR
file
Current POSIX.1 2001 revision of the tar standard removed the old limitation
of 8 GB of maximum archive size for tar archives defined in
POSIX.1 1988 standard
Features of TAR file
format
TAR
file format doesn't
feature native data compression, so TAR archives are often
compressed
with an external utility like, but not only, GZip, BZip2, XZ (using
7-Zip / p7zip LZMA / LZMA2 compression algorithms), Brotli, Zstandard,
and similar
tools to reduce archive's size, i.e. for more compact backup, or
smaller software distribution package.
Compressed TAR file
extensions
Compressed
tar files
can be found named with single extension, e.g. TGZ, TBZ, TXZ, TZST, or
with double file extension,
e.g. TAR.GZ, TAR.BR, TAR.BZ2,
TAR.XZ, TAR.ZST.
Adding items to a tarball before compression stage is quivalent to
using solid compression,
which can be beneficial for optimizing output size.
Similarly, TAR also does
not natively support cryptography, but it is possible to compress the
TAR package with a compression format providing file encryption features
such as zip, 7z, arc, pea.
Use cases for TAR
file format

|
When
it is recommended to use TAR format: it is a good choice for
distributing data on
Linux and
other Unix-like systems, combining it with .gz / .bz2 / .xz / Brotli /
Zstandard compression, in order
to
save bandwidth - if relevant for the intended use. |

|
PeaZip fully support creation and
extraction of TAR files on Windows and Linux systems.


Read more
about .tar extension: TAR specifications on GNU
software directory, TAR
file format
specifications on GNU
software directory, TAR
file format Wikipedia
entry, GZip Wikipedia
entry, GZip , BZip2 , BZip2 , Google Brotli , Google Brotli , and
Facebook Zstandard , and
Facebook Zstandard compressors' official domains.
compressors' official domains.
Legitimate use of double file extension
PeaZip can handle and create files with double
extension; most common cases for having have a file with two extensions
are

|
Compressed
containers
When a
compression only algorithm - most common ones are GZip Deflate compression, Brotli compression, BZip2 compression, LPAQ compression, Zstandard compression
or 7-Zip's lzma XZ compression -
is
applied to
multiple files, which consequnetly needs to be
consolidated into a single archive - most times a TAR file -
before the compression step (resulting in equivalent of solid mode
compression).
This result in the first step archiving extension (e.g. creating a TAR archive file) being
pre-pended to second step compression extension (e.g. XZ).
Extracting
compressed tar files
(TAR.GZ / TAR.BR / TAR.BZ / TAR.LPAQ, TAR.XZ / TAR.ZST) could be
treated as
atomic,
single step operation, but usually (as in PeaZip, 7-Zip and other
archival utilities) extraction
of compressed TAR files is a two step
process which firstly uncompress the TAR archive, and then unarchive
the contained files and folder structure.
|

|
Spanned
multi-volume archives
File spanning is
applied (often in a single pass) to output archive,
creating a set of volumes of desired size, with a numerator in the file
extension to declare what is the first volume and the progressive order
of data chunks, in example .R01, .Z01, etc
Some splitting standards adds the numerator information in a separate
extension, before or after usual archive extension, in example .7Z.001,
.7Z.002, .7Z.003 etc.
|
Risks, security issues of "Hide known file
extensions" option
A completely unrelated
use of double file extension spread after Micorsoft set "Hide known
file types extensions" option enabled by default for Windows XP
and
newer systems - this is still the default behavior on Vista, 7, 8, 10 -
opening the ground for attack exploiting hidden files extensions.

|
This option allows an
attacker to trivially add a file extension before
the true one in order to mask the real nature of the file - being the
last file extension hidden by default to end users by the system in
file browser and most applications following system's file browser
policies.
|
In example, an executable virus named attachment.exe can be renamed in
attachment.doc.exe.
By deafult, end user would be prompted "attachment.doc" (or any other
harmless file extension used by the attacker, i.e. .jpeg, .mpg), but
once clicked the file would be executed as .exe file (true file
extension) by the system.
In this way an executable file that should trigger a great level of
awareness and caution from user (e.g. .exe, .scr, .bat, .vb, .js...)
can be easily masked as harmless, common, file type to mislead end user.

|
PeaZip
file and archive browser never hide file extension, avoiding
this type of forgery.
Moreover PeaZip warns each time an executable or script file is being
executed from an archive, in this way 1) the user is made aware of the
potentially harmful nature of the file 2) the user can evaluate to
extract the whole archive before, as executable and script
files could need some archived resources (i.e. dll) to be available in
uncompressed form before properly running.
|
Sometimes files with double extension are treated as suspicious ones,
but if it is the right case for executable ones (exe or script file
type as last extension), it is definitely NOT the case for archive
files with double extension, being TAR.something very common file types
- especially on *x systems.
Read more about this topic: what are file
extensions , list of
known file
types , list of
known file
types , TAR , TAR archive
format, which usually comes with a second extension (tar.gz, tar.bz)
declaring the compression scheme applied to the tar container. archive
format, which usually comes with a second extension (tar.gz, tar.bz)
declaring the compression scheme applied to the tar container.
|
|
|
|
|
|
.TAR
|
no
maximum size POSIX.1 2001, previously GB max size POSIX.1 1988 |
|
|
SPEED 
Tar format features extremely fast speed: archiving to TAR file is
equivalent - in speed - of
merging files, faster than raw file
copy as the process avoids overhead of creating a new filesystem
entry for each file. If compression is applied in the pipeline of the
job, it will be likely the speed performance limitating factor.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMPRESSION
RATIO 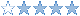
Tar file type is not meant to provide compression, and rely on external
compressors in
pipeline (tar.gz, tar.br, tar.bz, tar.xz, tar.zst) from which depends
the results in
terms of compression ratio.
|
|
ADVANCED
OPTIONS 
Tar standard is meant to provide only archiving of data and metadata.
Other features are
delegated, by specification's design, to external programs pipelined to
Tar command.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Synopsis: What is TAR file
format. What are TGZ, TBZ, TXZ file extenssions. Features and
specifications of tar archive type and related compressed tar file
types as tar.gz, tar.bz2, tar.xz. What are files types with double
extensions.
Topica: TAR file extension
specs, what are tgz / tar.gz, tbz / tar.bz2 formats
PeaZip > FAQ > What is
TAR file format, TGZ TBZ TXZ extensions
|


 , list of
known file
types
, list of
known file
types , TAR
, TAR archive
format, which usually comes with a second extension (tar.gz, tar.bz)
declaring the compression scheme applied to the tar container.
archive
format, which usually comes with a second extension (tar.gz, tar.bz)
declaring the compression scheme applied to the tar container.